if the irrational number
a +
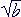 is a root then
is a root then a -
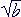
is also a root.
Suppose we know that 2 +
 is a root. What a is polynomial with this root?
is a root. What a is polynomial with this root?Since we know
2 -
 is also a root we know, through our Factor Theorem that
is also a root we know, through our Factor Theorem that(x - (2 -
 )) (x - (2 +
)) (x - (2 +  )) = 0
)) = 0So :
x2 - 2x +
 x - 2x + 4 -
x - 2x + 4 -  x -
x -  x - 2
x - 2 - 3 = 0
- 3 = 0Which equals : x2 - 4x + 4
Another way to look at this is to start with the equation.
Take x3 + 5x2 + 11x + 15
If you guss one root is 3 and try it with synthetic division, you find out it factors to
(x -3)(x2 + 2x + 5)
When we use the quadratic formula to factor x2 + 2x + 5
we find the roots are -1 + sqrt(-4) or -1 - sqrt(-4)
which is -1 + 2i or -1 - 2i
These two roots are imaginary. They don't hit the x line.
So, one of our roots is real and the other two are imaginary. Note : if we have 1 imaginary root then by definition we have two, because in the quadratic formula we have -b +- sqrt(discriminant). If the discriminant is negative then we have two imaginary roots.